The BRICS nations—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—have emerged as powerful players in the global economy. Initially formed to enhance economic cooperation among major developing countries, BRICS is now reshaping global trade, finance, and geopolitical influence. With the expansion of BRICS in 2024 to include Egypt, Iran, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Ethiopia, the bloc’s economic footprint has grown significantly.

BRICS and the Global Economy
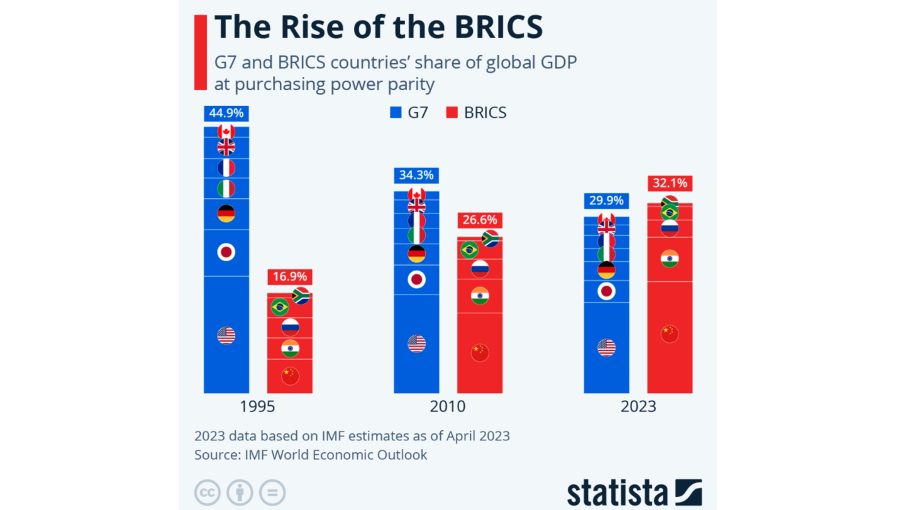
BRICS economies collectively contribute over 31.5% of the world’s GDP, surpassing the G7 nations in purchasing power parity. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), these nations are expected to drive global growth in the coming decade. The BRICS New Development Bank (NDB) has also played a key role in funding infrastructure projects in member countries, reducing reliance on Western financial institutions.
Trade and De-Dollarization Efforts
One of BRICS’ primary goals is to reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar in international trade. Recent agreements between China, Russia, and Brazil to conduct trade in local currencies highlight this shift. The introduction of a potential BRICS common currency is also under discussion, which, if implemented, could challenge the dominance of the U.S. dollar in global markets. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) has been closely monitoring these developments.
Geopolitical Influence and Expansion
The recent inclusion of new member states has strengthened BRICS’ geopolitical influence, allowing it to compete with Western alliances like the G7 and NATO. The bloc has been advocating for a more multipolar world order, challenging U.S. and European dominance in global affairs. According to a report by The Diplomat, BRICS aims to provide an alternative to Western-led institutions like the World Bank and IMF.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite its growing influence, BRICS faces challenges, including:
- Internal Political Differences: Conflicts between India and China, as well as differing national interests, hinder deeper economic integration.
- Economic Disparities: While China is the dominant economic power within BRICS, other members have relatively smaller economies, creating imbalances in decision-making.
- Lack of a Unified Financial System: The absence of a common financial framework limits the bloc’s ability to implement monetary policies effectively.
The Future of BRICS
As BRICS continues to expand and push for financial independence from Western institutions, its role in shaping the global economy will only grow. The bloc’s success will depend on its ability to overcome internal differences and establish stronger economic and political frameworks. With increasing investments in infrastructure, digital economy initiatives, and trade partnerships, BRICS is positioning itself as a key player in the future of global governance.
Conclusion
From economic cooperation to geopolitical influence, BRICS is redefining the international landscape. As the bloc continues to evolve, its impact on global trade, finance, and diplomacy will be crucial to watch. With ongoing efforts toward de-dollarization and financial independence, BRICS nations are steadily challenging Western economic dominance, marking a significant shift in global power dynamics.